Carbon Fiber vs Aramid Fiber: Everything You Need to Know
👁 Reads: 4723
Carbon fiber and aramid fiber are two popular types of high-performance fibers. These are used in various industries and are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals. However, despite their similarities, these fibers have distinct differences that affect their performance and application. In this article, we'll explore the differences between carbon fiber and aramid fiber and their pros and cons.
Is Aramid Fiber the Same as Carbon Fiber?
No, aramid fiber is not the same as carbon fiber. While both fibers are classified as "advanced composites," they have different chemical structures and properties.
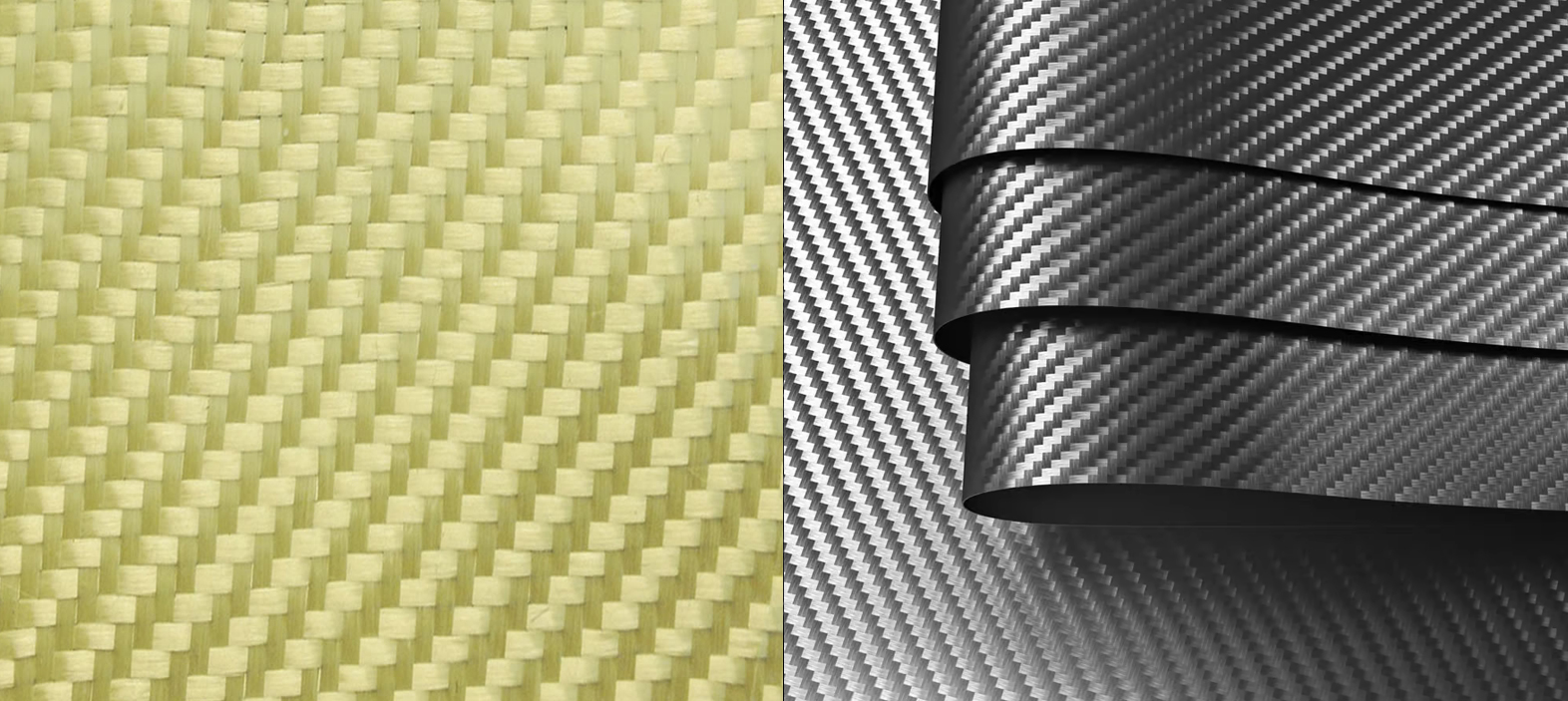
Carbon fiber is made of thin strands of carbon atoms, which are tightly bound and oriented in a specific direction. The carbon fibers are then woven into fabrics or mats and impregnated with resin to form composite materials. It is known for its high tensile strength, stiffness, and low weight.
Aramid fiber, on the other hand, is a type of synthetic polymer that contains aromatic rings in its molecular structure. The most well-known fiber is Kevlar, which is used in bulletproof vests, helmets, and other protective gear. Aramid fiber has excellent resistance to impact, abrasion, and heat, but is less stiff and strong.
Carbon Fiber vs Kevlar
Kevlar is a brand name for a type of aramid fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s. It is widely used in ballistic protection, such as bulletproof vests, helmets, and vehicle armor. Kevlar has a tensile strength of around 3.6 GPa (gigapascals), which is five times stronger than steel on a weight-to-weight basis.
Compared to carbon fiber, Kevlar has a lower stiffness and strength, but higher impact resistance and toughness. Kevlar is also more resistant to heat and chemicals. However, Kevlar is not as widely used in structural applications, due to its lower strength and stiffness.
Carbon fiber manufacturers supply the composite material for applications in aerospace, automotive, and sports industries for its high strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and fatigue resistance. Carbon fiber has a tensile strength of around 3.5-7 GPa, depending on the grade and manufacturing process. Also highly resistant to fatigue and corrosion, making it suitable for long-term use in harsh environments.
Carbon fiber is more expensive than Kevlar, due to its complex manufacturing process and higher demand. However, it is also more versatile and customizable, with different grades, weaves, and finishes available for specific applications.
Pros and Cons of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a composite material that has applications in various industries depending on the product. Take a look at both pros and cons to make an informed decision.
Pros:
- High strength-to-weight ratio: One of the strongest materials available, while also being lightweight.
- Stiffness: The characteristic of high modulus of elasticity, means it is very stiff and resistant to bending.
- Fatigue resistance: Carbon Fiber Products can withstand repeated stress cycles without breaking down or losing strength.
- Corrosion resistance: The composite material is resistant to most chemicals, including acids and alkalis.
- Customizable: The scope of being tailored to specific applications, with different grades, weaves, and finishes available.
Cons:
- Expensive: In aspects of cost, the material is more expensive than most other materials, due to its complex manufacturing process and high demand.
- Brittle: Easily prone to cracking under high impact or stress loads.
- Conductive: The electrical conductive characteristic can cause problems in some applications.
- Labor-intensive: The production requires skilled labor and specialized equipment, which can increase costs and lead times.
Pros and Cons of Aramid Fiber
Choosing Aramid Fiber for some composite products depends on the use and application of the end product. Knowing about the pros and cons of aramid fiber will help you make an informed choice.
Pros:
- Impact resistance: This characteristic makes it suitable for protective gear and other impact-resistant applications.
- Abrasion resistance: Highly resistant to abrasion and wear, the composite material is useful for products that experience a lot of friction.
- Heat resistance: The fiber composite can withstand high temperatures, making it useful for applications where heat resistance is critical.
- Chemical resistance: Due to the properties of being resistant to chemicals, it is used for applications where exposure to chemicals is likely.
Cons:
- Lower strength and stiffness: Less stiff and strong in comparison to other composites, Aramid fiber has limited use in structural applications.
- Moisture absorption: This particular characteristic affects its performance when exposed to moisture.
- Limited customization: With fewer grades and finishes available when compared to carbon fiber, it is limited in versatility.
- Expensive: More expensive than many other materials, which can limit its use in some applications.
Applications of Carbon Fiber and Aramid Fiber
Carbon fiber and aramid fiber are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Carbon Fiber Applications:
- Aerospace: Used extensively in the aerospace industry for structural components, such as wings, fuselages, and landing gear.
- Automotive: A preferable choice for high-performance cars for body panels, frames, and suspension components to reduce weight and improve performance.
- Sports equipment: Used for the design of tennis rackets, golf clubs, and bicycles, to improve performance and reduce weight.
- Wind energy: The composite material is used in wind turbine blades to reduce weight and increase efficiency.
Aramid Fiber Applications:
- Protective gear: Used in bulletproof vests, helmets, and other protective gear to provide impact resistance.
- Industrial applications: Applied in the design of conveyor belts, hoses, and gaskets, due to its high abrasion resistance and heat resistance.
- Aerospace: Effective in aerospace applications, such as aircraft tires and rocket motor cases, due to the high strength and heat resistant characteristics.
- Sporting goods: It is used in sporting goods, such as skis and snowboards, to provide impact resistance and durability.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber and aramid fiber are both high-performance fibers with unique properties and applications. Carbon fiber is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for structural applications in aerospace, automotive, and sports industries. Aramid fiber, on the other hand, is known for its impact resistance, abrasion resistance, and heat resistance, making it suitable for protective gear and industrial applications. While both fibers have their advantages and disadvantages, they offer unique benefits that can improve the performance and durability of products in various industries.





